
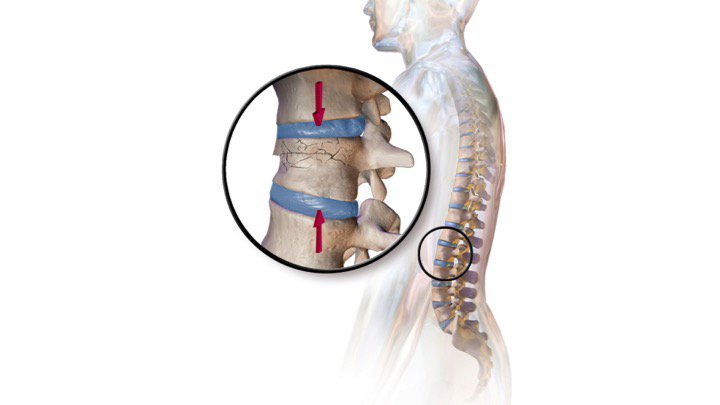
The bones of the spine are a common place for many types of cancers to spread. Metastatic tumors should be considered as the cause in patients younger than 55 with no history of trauma or only minimal trauma. People with healthy spines most commonly suffer a VCF through severe trauma, such as a car accident, sports injury or a hard fall. Occasionally, a VCF can be present with either minor symptoms or no symptoms, but the risk still exists for additional VCFs to occur. People who have had one osteoporotic VCF are at five times the risk of sustaining a second VCF. Although far more common in women, VCFs are also a major health concern for older men. The occurrence of this condition steadily increases as people age, with an estimated 40% of women age 80 and older affected. VCFs affect an estimated 25% of all postmenopausal women in the U.S. VCFs are the most common fracture in patients with osteoporosis, affecting about 750,000 people annually. In people with moderate osteoporosis, it usually takes increased force or trauma, such as falling down or attempting to lift a heavy object to cause a VCF. S2CID 43255503.In people with severe osteoporosis (weak, brittle bones), a VCF may be caused by simple daily activities, such as stepping out of the shower, sneezing forcefully or lifting a light object. "Metastatic disease in long bones: A proposed scoring system for diagnosing impending pathologic fractures. "Bone mineral density measurement and osteoporosis treatment after a fragility fracture in older adults: regional variation and determinants of use in Quebec".
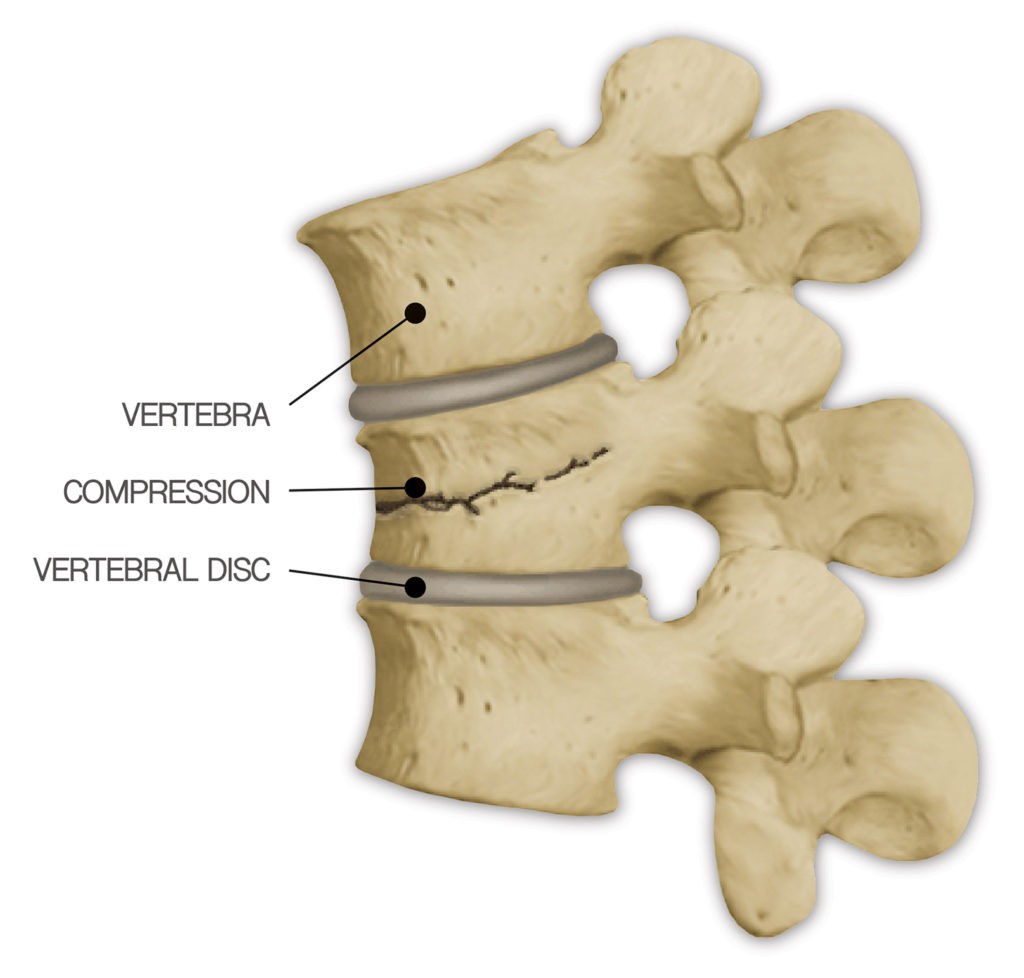
Fixation is done by internal fixation rather than conservatively, along with treatment of the underlying cause. Management īased on Mirel's score (if the score is more than 8), bone fixation should be done prophylactically. In circumstances where other pathologies are excluded (for example, cancer), a pathologic fracture is diagnostic of osteoporosis irrespective of bone mineral density. Bone atrophy secondary to diseases like polio.Pathologic fractures in children and adolescents can result from a diverse array of disorders namely metabolic, endocrine, neoplastic, infectious, immunologic, and genetic skeletal dysplasias. In a pathological compression fracture of a spinal vertebra fractures will commonly appear to collapse the entire body of vertebra. Pathological fractures present as a chalkstick fracture in long bones, and appear as a transverse fractures nearly 90 degrees to the long axis of the bone. This definition arises because a normal human being ought to be able to fall from standing height without breaking any bones, and a fracture, therefore, suggests weakness of the skeleton. There are three fracture sites said to be typical of fragility fractures: vertebral fractures, fractures of the neck of the femur, and Colles fracture of the wrist. Only a small number of conditions are commonly responsible for pathological fractures, including osteoporosis, osteomalacia, Paget's disease, Osteitis, osteogenesis imperfecta, benign bone tumours and cysts, secondary malignant bone tumours and primary malignant bone tumours.įragility fracture is a type of pathologic fracture that occurs as a result of an injury that would be insufficient to cause fracture in a normal bone. This process is most commonly due to osteoporosis, but may also be due to other pathologies such as cancer, infection (such as osteomyelitis), inherited bone disorders, or a bone cyst.
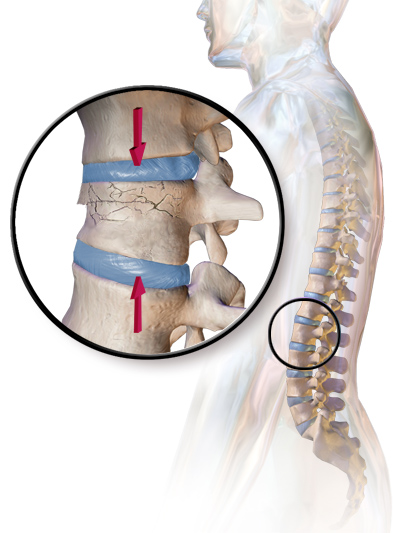
Pathological fracture of the humerus in a patient with metastasis of renal cell carcinomaĪ pathologic fracture is a bone fracture caused by weakness of the bone structure that leads to decrease mechanical resistance to normal mechanical loads.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
